

"Sustainable fuels replace or greatly reduce the mining or drilling of fossil fuels from below the earth's surface. They are produced from renewable and/or alternative feedstocks, such as plant, vegetable or industrial waste.
Sustainable fuels include biofuels such as hydrotreated vegetable oil (HVO), or bioethanol, Aviation fuel, biodiesel and synthetic fuels (synfuels) such as ammonia or methanol. Sustainable fuels could account for 37% of energy in demand in transportation by 2050"

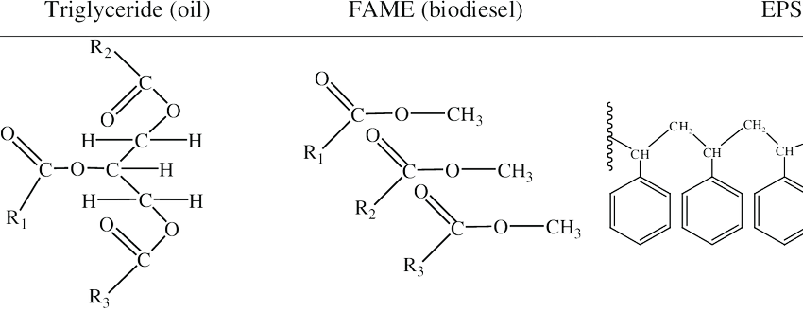
The basic biodiesel chemical formula is C17H34O2, with the ester group –CO2CH3 at the end of the long carbon chain.
Biodiesel is made when a triglyceride molecule (oil or fat) reacts with 3 molecules of an alcohol (usually methanol or ethanol) to produce 3 molecules of biodiesel (also called “methyl esters” or “ethyl esters”) and one molecule of glycerol. The composition of biodiesel is mostly triglycerides that are classified as esters. The esters are processed through transesterification. Biological oils from vegetable and animal fats — this includes used oils from cooking — react with short-chained alcohols and a catalyst under heated conditions through a process of tranesterification that converts the esters, the long-chain fatty acids, to biodiesel and glycerin.


When we talk about a “carbon footprint” we are referring to human activity that produces carbon dioxide (CO2) and thus contributes to climate change - activities like burning fossil fuels for heat, electricity, and transportation. We can reduce our carbon footprint by using biofuels such as biodiesel and ethanol. Because these fuels are made from plants that absorb carbon from the atmosphere as they grow, biofuels add less new carbon dioxide to the atmosphere than do fossil fuels.
They can decrease Green House Gases emissions between 56-96%, the equivalent of planting 1.9 billion trees. It can also cut global warming pollution by 80-90% when compared to petroleum diesel.

Global biodiesel production is projected to increase to 50 bln L by 2030, driven principally by Indonesia’s mandate to increase over the initial projection years. Feedstock for biofuel products vary from country to country. Global biofuel production will continue to be dominated by traditional feedstock despite the increasing sensitivity to the sustainability dimension of biofuel production observed in many countries
Since 2000, the share of biodiesel and hydro treated vegetable oils (HVOs) in total biofuel production has increased nearly 10-fold, from 3.3% in 2000 to nearly 32% in 2020, but bioethanol still accounts for 2/3 of total production.
In 2020, first generation biofuels still covered most of global production, with corn and sugar cane accounting for 64% and 26% of global bioethanol production, respectively, and vegetable oils for 77% of global biodiesel production."

"As biodiesel is known as an alternative to diesel fuel, there are other uses. Many assume that the material is used just for transportation. But biofuel can provide hydrogen, clean up oil, work as cooking oil and more. Biofuels can work as an alternative to replacing energy needs from vehicle fuel to central home heating.

To ensure as stabile climate and make real on the commitment of the Paris Agreement UNEP has identified six sectors with the potential to reduce emissions enough to keep the world below the 1.5°C mark.
UNEP has come up with 6 sector solution that can reduce carbon dioxide emissionns and limit the temperature rise to 1.5 degree celcuis.